Let's take a look at what Lumps and Bumps are.
Benign Lumps
Benign tumours are non-cancerous and do not spread to other parts of the body and may include,
- Cysts
- Nodules
- Lipomas
- Haematoma
- Hemangioma
- Papilloma
Malignant Lumps
Malignant tumours are cancerous with the potential to invade the surrounding tissue and spread to other parts of the body. Some of the benign lesions above may be malignant, a good history, clinical examination and occasionally imaging or biopsy is needed to differentiate.
We can perform lipoma removal for small lesions under local anaesthetic in our office.
Causes of Lumps
Lumps and Bumps may be caused by
- Infection
- Acne
- Cysts
- Boils
- Moles
- Lipomas
- Masses
- Skin rash
- Skin cancer
Types of Lumps & Bumps
Cysts
A cyst is a lump or sac that is filled with fluid, jelly-like material or gas. There are many different kinds of cysts.
The most common kinds of skin cysts are:
- A Dermoid Cyst is a lump that is made up of the cells that grow to be skin. These cells did not grow properly and form a bag or sac that may contain sweat, oil, hair or skin particles. These lumps are commonly found on the head and neck area. This kind of lump can get bigger over time. Sometimes the fluid inside can become infected and the lump becomes red, swells quickly and is painful.
- A Sebaceous or Epidermal Cyst is a lump caused by a blocked oil gland. It is filled with oil and the cells that make oil for the hair shaft. This lump is commonly found on the head but can occur anywhere. This kind of lump can get bigger over time and can become infected.
- A Ganglion Cyst is a lump that is made up of the skin and fluid that covers joints. They are commonly found on the wrist. These lumps frequently change in size. They may be large one day and gone several days later.
Masses
A mass is a lump that is caused by an overgrowth of tissue.
- Pilomatrixoma is a lump caused by an overgrowth of cells that grow into skin and hair. It is similar to an epidermal cyst but it is solid.
- Hemangioma is a mass caused by abnormal growth or formation of blood vessels. Capillary Hemangiomas are bundles of abnormal blood vessels that are close to the top layer of the skin. They may be red or purple in color.
- Cavernous Hemangioma is found in the deeper layers of the skin and may have a faint purple or blue color. Hemangiomas are often present at birth or shortly after. They may get bigger over the first 6 months. They gradually get smaller, often disappearing completely durin
- Hematoma is a lump caused by a collection of old blood. If the blood is trapped under the skin it may take a while for the blood to be absorbed by the body. Sometimes the blood crystallizes and becomes hard
- Abscess is a lump caused by a collection of infected fluid or pus
- Granuloma is a lump caused by an overgrowth of inflamed tissue. This tissue may grow if there is something under the skin the body is trying to get rid of like a foreign body
Lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are soft nodules of tissue and they are a part of the lymphatic system.
Lymph nodes help to identify germs, infections, and other foreign substances that invade our body. They are found throughout the body and become swollen from infection or other inflammatory conditions of the body.
Diseases of the lymph node may be caused due to infection, inflammation, an abscess, or cancer. Some of the diseases of the lymph nodes are
- Lymphadenopathy – Refers to swelling or enlargement of one or more lymph nodes occurring due to local or systemic conditions or diseases. Lymphadenopathy can be localized or generalized.
- Hodgkin’s disease–Cancer of the lymph tissue found in the lymph node that may spread to spleen. Liver, bone marrow, and other organs.
- Lymphadenitis – It is an infection of the lymph nodes and is a common complication of bacterial infections.
Enlarged or swollen lymph nodes are frequently found in the neck, armpit, under the jaw or chin, behind the ears and on the back of the head.
Swollen lymph nodes are diagnosed by physical examination to check palpable lymph nodes for size, texture, and tenderness and other features.
Pain medications such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen may be prescribed to relieve pain and to reduce the swelling. Infections are usually treated with antibiotics and antiviral medicines. And cancer of the lymph node is treated with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or surgery.
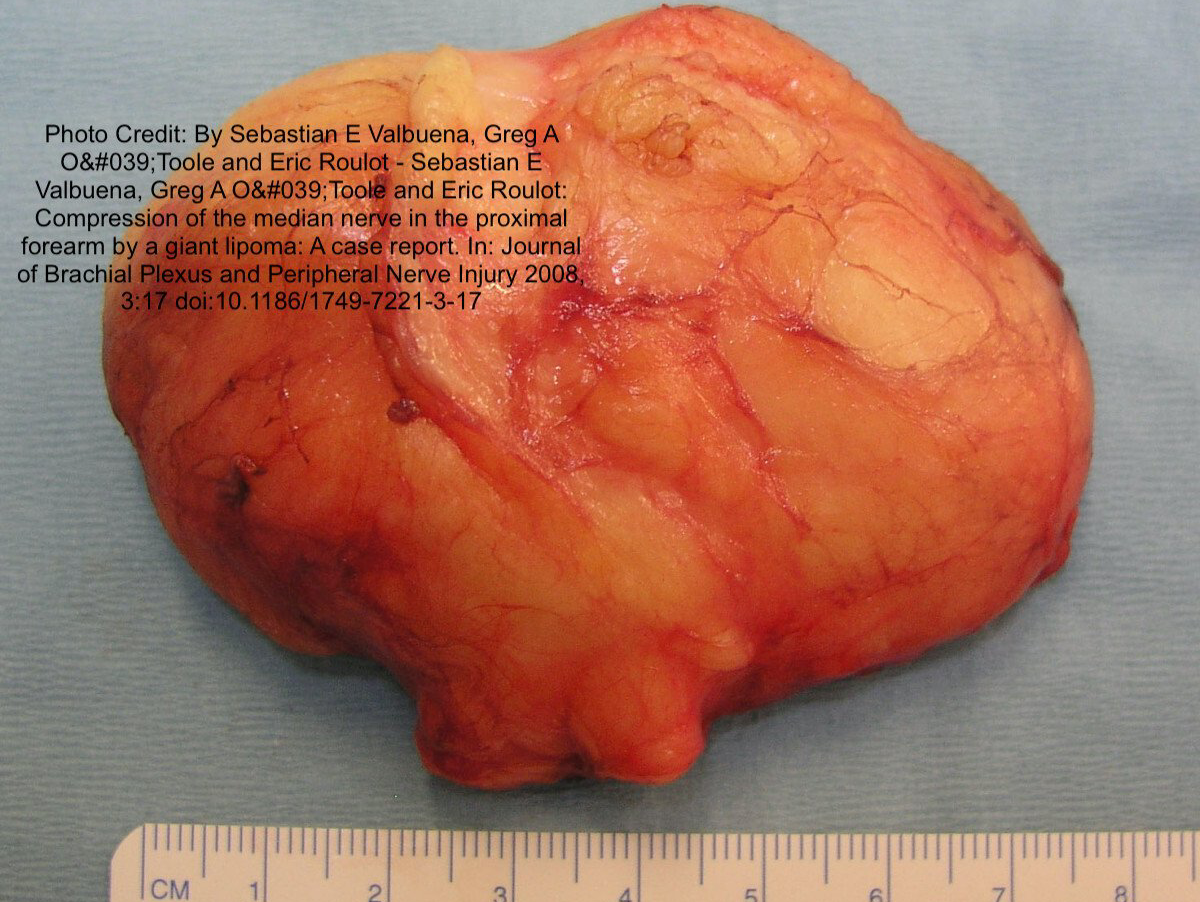
Lipomas
A Lipoma is a lump caused by an overgrowth of fat cells. These lumps generally do not change in size, they are not painful and are not harmful. They are unusual in children.
Lipomas are slow growing tumours that arise from fat cells. They are soft or rubbery, round, movable, flattened, and are found under the skin. They are the most common non-cancerous tumours occurring in adults.
They usually grow in the face, neck, shoulders, back, or arms and may develop between 40 and 60 of age.
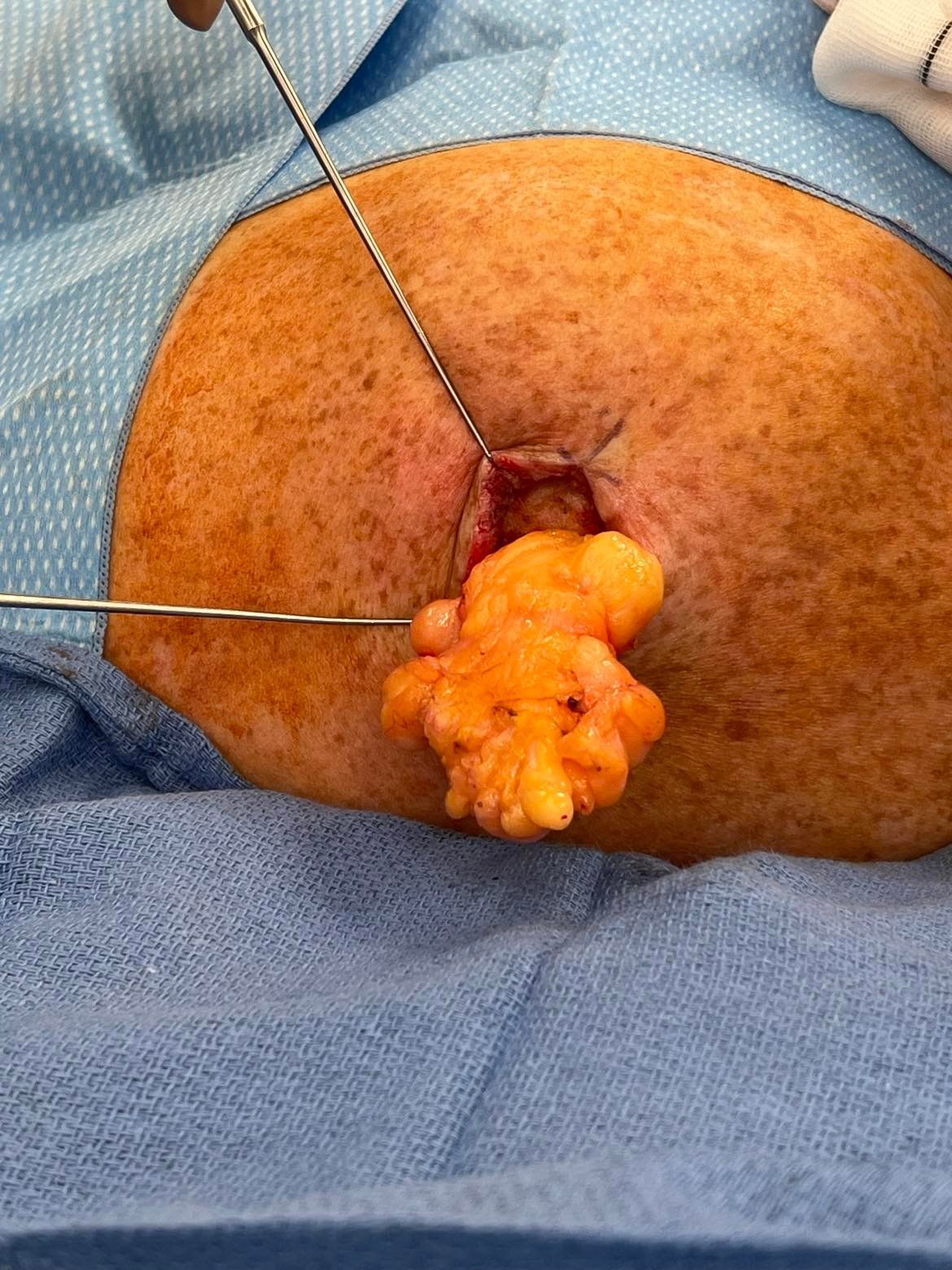
Treatment for lipomas is required if it becomes painful or restricts movement, or causes an embarrassing lump.
Some of the techniques in surgical removal of lipomas are:
- Enucleation: The lipoma is removed through surgery and is enucleated (removal of nucleus) through the incision using a curette.
- Surgical excision: In this procedure a hemostat or Allis clamp is used to provide grip for lipoma removal.
- Hemostat or clamps are attached to the lump to provide traction for easy removal of lipoma.
- Narrow hole extrusion technique (skin punch): Skin punch creates a narrow hole in the lipoma from which a curved hemostat is inserted and the lipoma is removed
Risks of general surgery include
- Infection
- Formation of hematoma
- Injury to the nearby tissues, blood vessels, or nerves
- Scarring
- Permanent deformity due to removal of large lesion
- Irritation and injury to the muscles
Dr. Sandra Krishnan’s lipoma removal clinic in Sydney is more than equipped for small general surgical procedures which can be done in a clean environment with sterile precautions.
Call us on
(02) 94675400.